|
Назад
Главная страница
Оглавление
Далее.
Russia's original ...
The period of crushed skulls.
1. The period of crushed skulls.
Here is what Anatoly Klyosov writes.
Approximately
4500-4000 years ago something happened in Europe, as a result of
which the haplogroup R1a1 from Europe practically disappeared.
As, by the way, at the same time both haplogroup I1 and largely
haplogroup I2 disappeared.
Shortly thereafter, Europe was populated with carriers of the
Turkic-speaking R1b (mainly its subgroups R1b1b2).
The main reasons could be two - or almost complete extermination of
other haplogroups with R1b carriers, or between 4000 and 4500 years
ago in Europe there was a major natural cataclysm, and the
Turkic-speaking R1b1b2 settled already practically deserted Europe.
You can find evidence in favor of one and the other assumption.
On the possibility of the first say the finds of many ancient human
remains with crushed skulls in Scandinavia, which date back to about
the same time that even got the conventional name "the period of
crushed skulls."
It is characteristic that many finds revealed crushed skulls of
women and children (Lindqvist, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1997, 1998).
This resonates with the finding in Germany of a group of 13 people,
most of whom were children and women, most (including children) with
shattered skulls and stone arrowheads stuck in the bones, dating
back to 4600 years ago.
Two boys (ages 4-5 and 8-9 years) and men aged 40-60 years were able
to determine the haplogroup, and in all three it was R1a (Haak et
al, 2008).
The analysis of the place of the event showed that women, the
elderly and children were killed during the absence of adults,
apparently by a hostile tribe.
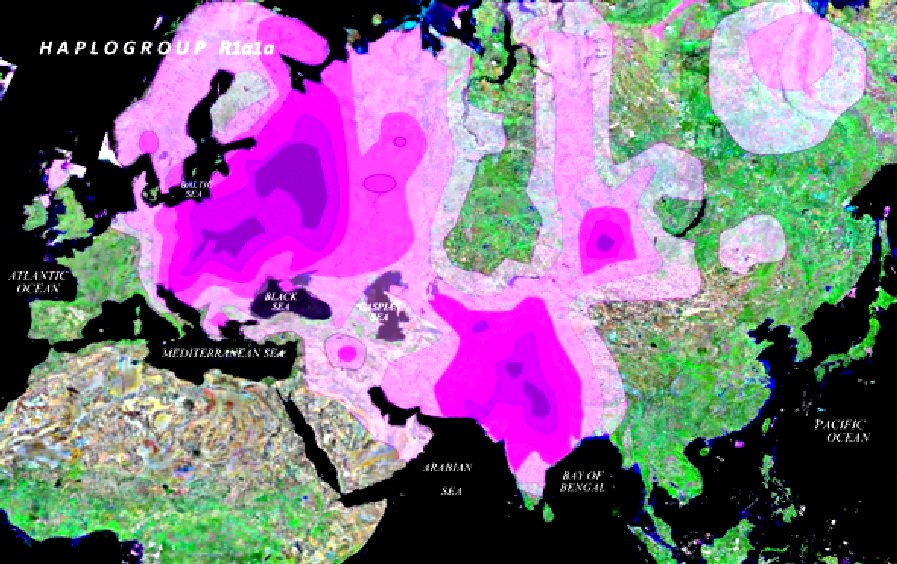
Figure 1.
Modern areas of residence of the Aryan haplogroup R1a.
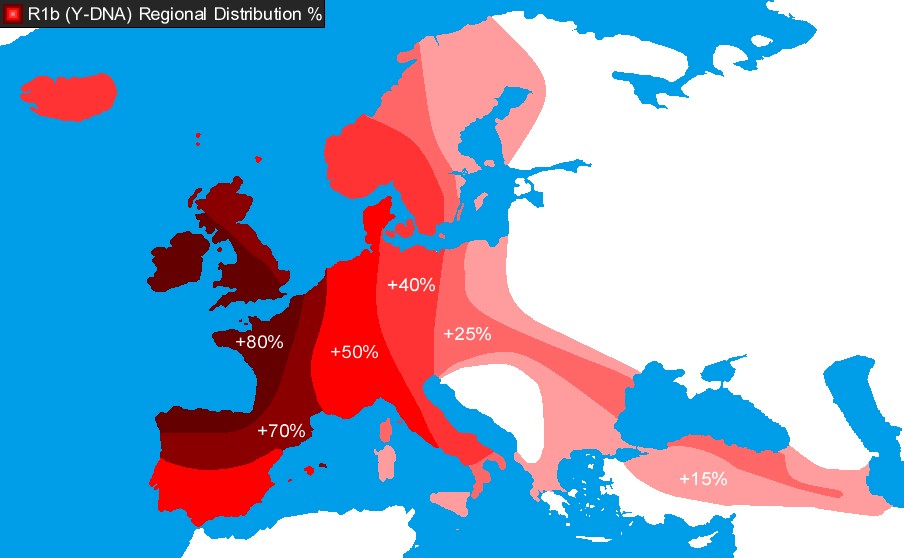
Figure 2.
Modern habitats of western haplogroup R1b.
We
return to Europe from 4500-4000 years ago.
So, the variant of extermination of carriers of haplogroups R1a1 and
I has a historical basis.
Moreover, in Scandinavia the haplogroup I1 was (then and now)
especially widespread, so that the crushed skulls in Sweden could be
primarily related to them.
But one can not exclude a major natural cataclysm in Europe between
4,500 and 4,000 years ago, and there is a lot of literature about it
that is so vast that we will not dwell on it now.
We refer only to geophysical work (Keenan, 1999), in which there are
hundreds of references on this topic.
According to the author, this was, in all probability, the
largest destructive event in the history of civilization since the
Ice Age, and it "enveloped the prevailing part of the northern
hemisphere" (ibid.).
Apparently,
according to the standard scheme, the period of "fragmented skulls"
is associated with the "Indo-European invasion", not realizing that
the "Indo-Europeans" (PS = Aryans) already lived in Europe 12
thousand years ago, and there was no "invasion" of them from the
west .
Later, from
the end of the 3rd millennium BC.
and during the next one and a half millennia, before the transition
to India and Iran, the vector of their migrations was directed to
the east.
The so-called "Kurgan theory" to the "Indo-Europeans", that is, to
the R1a1 carriers, to the aria, had absolutely nothing to do with
it, but belonged to the R1b speakers who were Turkic-speaking, and
moved really westward and further south, across the Caucasus
to Asia Minor and further to Europe, as described above, moreover, a
thousand or more years before the Aryans.
They also had nothing to do with Indo-, either linguistic or
migratory, and one can only wonder how such a theory could ever have
appeared.
As, however, and the "Anatolian" theory of the "Indo-European
ancestral home".
This will be discussed below.
Whatever
the reason, the haplogroup R1a1 practically disappeared from Europe
about 4500-4000 years ago, and the Turkic-speakers of the haplogroup
R1b populated the deserted Europe.
As shown in several lines below, almost all modern branches of
haplogroup R1a1 in Europe date from 2900-2500 years ago and later.
At the same time, there is evidence that the haplogroup R1a1 was in
Europe since 12,000 years ago.
Archaeological excavations revealed the haplogroup R1a1 in Europe
(Germany) 4,600 years ago (see above).
In other words, in Europe with R1a1 there is a gap between the
middle-end of the 3rd millennium BC.
(4500-4000 years ago) and continuing one thousand and a half
thousand years.
At the same time, in respect of R1b1b2 in Europe there is no gap,
their settlement is continuous flow from 4000-4200 years ago,
without stopping.
(P.S., these thousand and a half thousand years bring to mind the
memory of a thousand and a half thousand years, added by Scaligerian
historians - enemies.) However, at a superficial glance, there is no
connection here ... But if it's deeper ...! ...)
As a result, Europe, apparently, became a Turkic-speaking one.
R1a1 remained only on the Russian Plain, descendants of those who
moved there about 5 thousand years ago.
A few centuries later, about 3,500 years ago, the surviving
descendants by that time of the haplogroup R1a1 disappeared in
Europe would bring their haplotypes, and the Aryan language they
retained to the Urals and Central Asia, to India and Iran, to
Siberia.
The common ancestor of all these branches of haplogroup R1a1 lived
on the Russian Plain 4750 ± 500 years ago.
This is again the data of DNA genealogy with inevitable conclusions
of a linguistic nature.
It is known that in India and Iran was introduced the Aryan, the
pra-Indo-European language.
It should hardly be assumed that the same genus R1a1 brought
a certain other language to the Urals and South Siberia at the same
time.
The
repeated resettlement of Europe by carriers R1a1 occurred in the
period 2900-2500 years ago, that is, from the beginning to the
middle of the first millennium BC, and later.
This is how the life times of the common ancestors of the main European
DNA-genealogical branches look (Rozhansky and Klyosov, 2009), the
times in the years from the present time are indicated:
• European North-West 2925 ± 370 years ago
• North Carpathian 2800 ± 350
• Western Eurasian 2750 ± 370
• Central European 2725 ± 300
• West Slavic 2575 ± 300
• Southern Eurasian 2550 ± 320
• West Carpathian 2150 ± 300
• Scandinavian 1900 ± 400
• Northern Eurasian 1575 ± 260
This
was returned to Europe by carriers of inflectional, Indo-European
languages.
Apparently, for a number of regions this was the end of a past era
and the beginning of our era.
As a result of this resettlement, the Turkic European languages
were replaced by Indo-European languages, and this tipped the
scales towards the current European languages.
But this replacement left a large number of Turkisms in
personal names, names of items, individual terms.
It
is unlikely that the displacement of the Turkic languages by the
Indo-European languages in a foreign Europe was quick and
painless, or peaceful.
Usually, with such substitutions there are - in combination - a
number of factors, especially military, economic and political
(ideological) factors.
The military factor is not always mandatory, or rather not decisive,
but the last two factors are necessary.
Apparently, the carriers of the Indo-European languages coming
from the East convincingly (this is a broad concept) demonstrated to
the Turkic-speaking population of Europe of the last millennium of
the last era the advantages of their organization, the advantages of
a producing or more progressive economy, the level of education and
culture.
Only this could lead to the assimilation of another's (for the then
Turkic population of Europe) material culture and the transition to
another language.
This area
is still waiting for its researchers.
The fact that the branches of the genus R1a1 returned to
Europe from the Russian plain is evidenced by the fact that all
these combined European and Eurasian branches give a haplotype of
the ancestor from the Russian Plain, and the same age, approximately
4,900 years ago (Rozhansky and Klyosov, 2009).
Thus,
repeating the statement Yu.N.
Drozdova "... it is impossible to find any ancient source in which
any traces of the stay of Indians or their kindred peoples in
European territory were recorded" It is worth noting that, despite
the ancient sources and their interpretation, the "Hindu" carriers
of haplogroups
R1a1 with its inflected "Indo-European" language, more
precisely, by that time already languages, returned to the beginning
of our era in Europe and brought back their languages.
The
genus R1a1 with its Aryan language passed to the Russian plain,
presumably from the Balkans, at the beginning of the 3rd millennium
BC.
Its migration vector was directed to the east, although the path
from the Carpathians to the southern Urals and to Central Asia for
this genus took fifteen hundred years.
It is clear that they
were not nomads.
It was a slow but steady settlement of the Russian Plain.
It was the spread of the Aryan language from the Baltic to the
Caucasus, and further to the Caucasus, Anatolia, the Hittites and
the Mitanni.
In those parts, the Aryan, Pra-Indo-European language came, judging
by the mutations in the haplotypes, about 3,600 years ago.
In this region, he remained, and if he advanced, then not to the
east, but to the south, to the Arabian Peninsula.
The share of R1a1-M17 in Russia, Iran, the Middle East and the
Arabian Peninsula, according to (Abu-Amero et al, 2009; Underhill et
al, 2009), is the following, see Fig.
5.
No
notable advances to the north or east from the Near East, the
Pra-Indo-European (R1a1) did not.
Transcaucasia, western Azerbaijan, or western Iran, and the whole of
the Near East were simply "dead ends" of the "pristo-Indo-Europeans"
stay 3600-3000 years ago.
The Arias came there again from the territory of Iran in the first
millennium BC, expanding the territories of their empires to the
Caucasus and Assyria.
But this was already the time of the oldest Iranian languages with
the transition to the average Iranian languages.
I recall that the haplogroups R1a1 were found in the
Andronovo archaeological culture, and the haplotypes were typical
modern haplotypes of ethnic Russians (Klyosov, 2009, and references
there, Klyosov, 2009b).
It
is for this reason that I continue to believe that there is a high
probability that the Basque languages represent the ancient Turkic
languages of the haplogroup R1b, brought to the Pyrenees about 4
thousand years ago, after a big round trip from Altai, through the
Volga-Ural and southern steppes, through the Caucasus, Anatolia
and the Middle East, through North Africa to further to Iberia.
And the fact that the Basque language remains for many linguists
"unclassified" reflects the position of S.E.
Malov "we would not understand them with our present knowledge;
we would not know any sound alternations, special phonetic
laws, and then the lexicon, especially for any realities of the
ancient Turks. "
If
the scheme proposed in this paper is correct, then the answer to the
question of S.E.
Malova - "I have no answer to the question: who is more ancient -
the Bulgarians, the Chuvash in the west (the Danube and the Volga)
or the Uighurs in the east - in Central Asia, or they are
simultaneous?" Is quite definite: the Uighurs in the east are much
older.
So, as inevitably follows from the above, the carriers of the
haplogroup R1a1, they are arias, they are also "Pra-Indo-Europeans"
moving from Europe, most likely from the Balkans, to the east from
the beginning of the 3rd millennium BC, populating the European
plain
(the age of the common ancestor of the Aryans in the Russian Plain
is about 4750 years), and further, with the founding of the
Andronovo culture 4000-3200 years ago, which overlapped the habitat
of the haplogroup R1b1 for a half or two millennia before (Botai
archaeological culture 5700-5100 years ago)
,
followed by the settlement of the southern Urals and Zaural
south Siberia and Altai up to northern China.
Haplogroup
R1b moved counter way, but long before that - on the Russian Plain
at least 8-5 thousand years ago, partially populating the Caucasus
already 6 thousand years ago, and at the same time moving to
Anatolia and further to the Middle East.
That is, they practically did not intersect with the
"Pra-Indo-Europeans", carriers of the haplogroup R1a1 in time, but
crossed in the same territories, in particular the Middle Volga,
Samara, Khvalyn, Ancient Amur, Surna, Andronovo cultures.
This caused misunderstandings of archaeologists and
linguists regarding the localization of the "Indo-European homeland"
both in the southern steppes of Russia, and in the Black Sea region
and in Anatolia.
As
the attentive reader has definitely noted, this article is not at
all about the Turkic languages.
It is quite obvious that the main provision of the article on the
Turkic speaking of R1b carriers is based on ONE, the only argument
is that there really is a Turkic substrate in Europe, and that there
are many Turkic languages in the Indo-European language, which,
according to some Turkologists, follows from the analysis of tests
by ancient authors. All.
Because if this situation is false or exaggerated, then there are no
other arguments about the Turkic-speakingness of R1b.
You can honestly write that the author is not a linguist,
and therefore simply trusted (or accepted as a working hypothesis)
this argument of the Turkologists.
Although
it remains that some non-European substrate in Europe was - this is
the Basque language, and Basque-like language over a large part of
Europe.
As the historian and linguist Indarby Byzov notes, in the
pre-Romanization and Celtic era, the Iberian Peninsula was inhabited
by Iberians, who were related to the Basque language.
They also inhabited the British Isles, Ireland and the western part
of France.
To the east of them, down to the Rhine lived Ligurians, who are also
identified with the Sino-Caucasian group (I. Byzov, private
communication).
But this again clearly haplogroup R1b, the culture of
bell-shaped cups, because it comes again from the Pyrenees in
Europe, following the path of migration of carriers of haplogroup
R1b1b2.
Hence,
we again come to existence in Europe 2nd millennium BC.
(if not Turkic) agglutinative language that was in the haplogroup
(genus) R1b1b2, and then all the provisions of the article are again
correct, only it remains to replace the word "Turkic" with
"agglutinative language of R1b carriers".
For example, the
language "erbin."
Which could be an ancient language, also agglutinative, and which
Turkologists could take for the Turkic language, analyzing the
ancient texts.
Maybe this will reconcile the situation, since both sides, the
"Iranians" and "Turkologists" were in some way wrong.
Our comment.
This chronology from Anatoly Klesov seems quite reliable.
It seems that the appearance later of some "emptiness" of the
population in Siberia and near the Urals is explained by outflow of
population in the region close to Western Europe.
The most
likely cause of outflow is climate.
But a higher culture of western Europe is also probable.
And to this, very likely, successes in the struggle against the
counteraction of Western European peoples.
If 4000 - 4,500 years ago, the west was oppressed by the
Proto-Slavs, then the reverse process started 3,000 years ago.
In this process, all the peoples inhabiting eastern Europe
participated.
Bulgars, Mordvins, Bashkirs, etc.
Later, they created in Europe a lot of states or autonomous
regions in the states.
It
is very likely that Western historians, copying the surviving
memoirs and documents, later gave their own feelings from the
invasion of the East Europeans for the sensation of the Russians
from the invasion of supposedly Mongol-Tatars.
This is evidenced by the fact that no burials of numerous
Mongol-Tatar leaders were found, which is explained by the supposed
wisdom of the Mongol-Tatars.
Say
no one should desecrate the leader's grave.
However, if we recall that the ancient Slavs burned the corpses of
the dead, everything falls into place.
That is, these Mongol-Tatars were Slavs.
The
strength of Russia was confirmed in all the counter-offensive of the
West, both the Knights of the Crusaders, and Napoleon and Hitler.
The East is stronger.
However, at the present time there is a real threat of revenge of
the West.
Because the Russians and the Slavs were less receptive to science
and technology, to discipline and hard work.
And also they were more aggressive with regard to their own
carriers of intelligence, in particular, to the Jews.
There is one more
hypothesis.
Everything known for the period of total reinterpretation of history
was sorted by the principle: the positive takes the west, the
negative is left to the east.
Therefore, all the horrors of the Mongol-Tatars were in the east.
It is possible that the action attributed to the ancient Sparta for
dropping weak babies from the rock, actually happened in the Slavs.
It is possible that this was a cleansing, including from a dwarfish
breed.
Which was in abundance after crossing with Siberian and Asian
dwarfs.
Confirmation is the breed of "Russian bear" and various epic heroes.
This is not an invention, the heroes in Russia and the Slavs exist,
it is enough to look at the champions in boxing, fights without
rules, wrestling, bar, etc.
And in the outskirts there are heroes and stronger, but not
everyone can reach the big arena, and the character is not suitable
for modern civilization.
It
seems that the well-known historical facts of the extermination of
Huguenots or heretics in Europe are the echoes of the "era of
crushed skulls."
The methods possibly applied by Western Europeans in their attack on
the Slavs are well illustrated by a well-known historical example.
When the leaders of all the Prussian tribes were gathered together
in one place for negotiations, and then they were cut.
This is one of the fragments of the epoch of crushed skulls.
It is presented in an encrypted form.
Furthermore.
The famous moment of the murder of David Goliath from the Bible by
splitting the skull with a stone thrown from the sling deserves
special attention.
It is possible that here is the main reason for the epoch of
fragmented skulls.
When western settlers from the Atlantic coast (mostly from
Turkic-speaking immigrants, about the same as Albanian settlers in
Serbia), led by intelligent Jewish advisers, generals and inventors,
armed with unknown Slavs with slingers, were well trained and broke
to the east.
There they successfully defeated the Slavic troops, destroyed
virtually all men (haplogroup R1a completely absent in France,
England, western Germany), but left strong and beautiful Slavic
women.
This is how the present-day West European nation was born, in beauty
and mind, not inferior to the Slavs, but not with the group R1a, but
with the group R1b.
And curiously, it was the R1b group that was more tolerant of the
presence of the Jews.
What caused a much larger percentage of Jews in Western countries
and their combined influence to be countries of a higher standard of
living, technology, culture, finally, football and tennis than the
Slavs. What we observe.
And one more
circumstance.
Historians especially do not pay attention to the cross-over of a
man of the modern type that took place in the era of resettlement
from Africa, with a dwarf type settled long before him.
About what the article "About the role of pygmies and dwarfs in
human evolution" is about.
But the overwhelming number of historical events and migrations is
connected with hybrids from dwarfs and gabers.
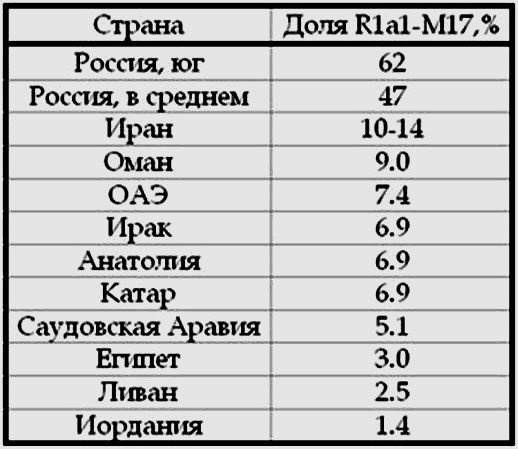
Figure 3. The
share of haplogroup R1a1 in the Asian and Arab countries.
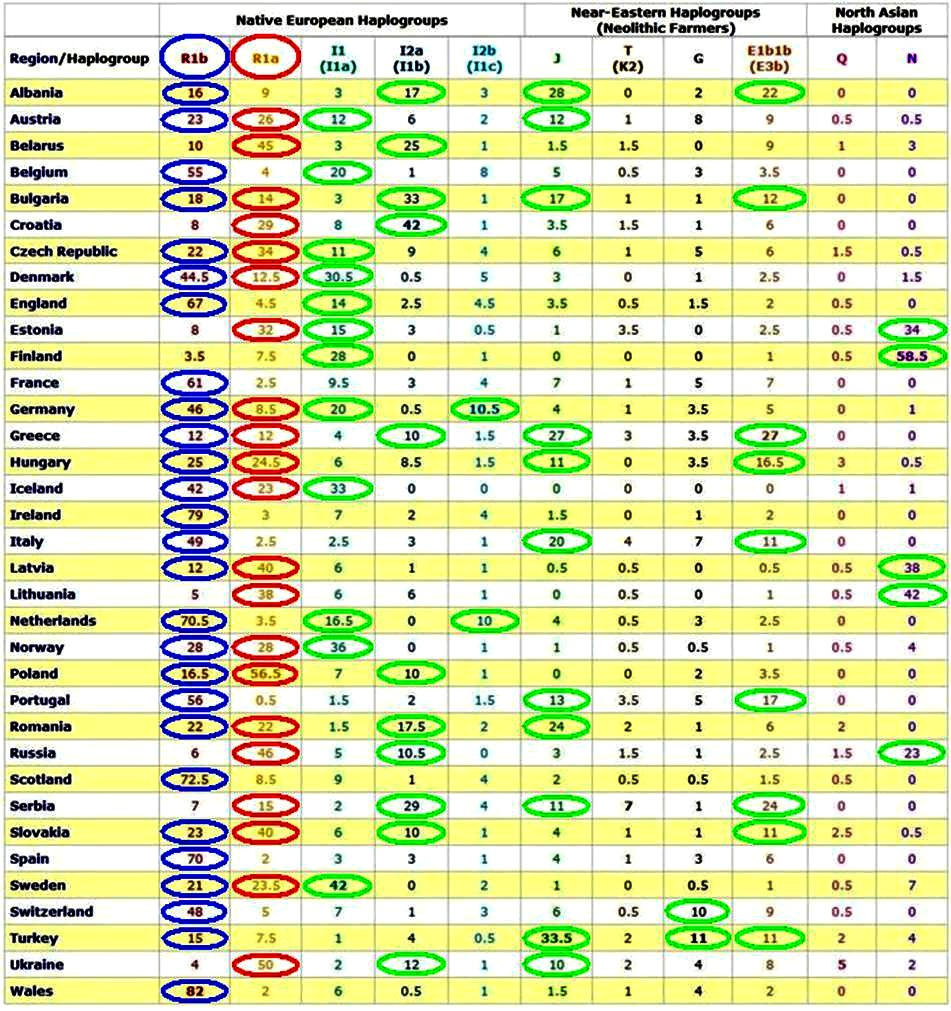
Figure 4. Table
of haplogroups in European countries. Significant interest is
allocated.
Назад
Главная страница
Оглавление
Далее.
|



