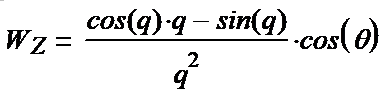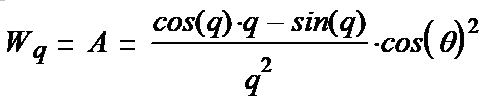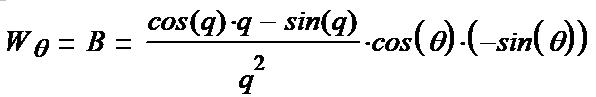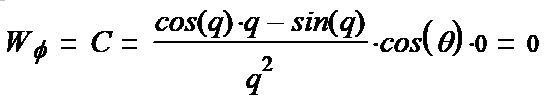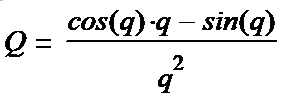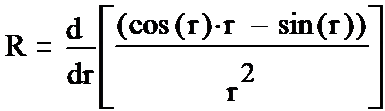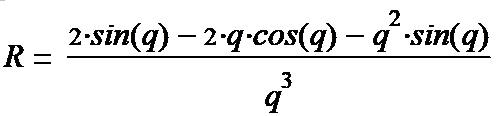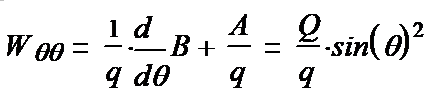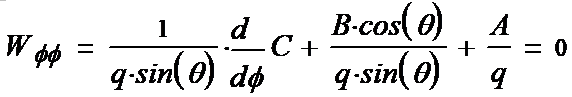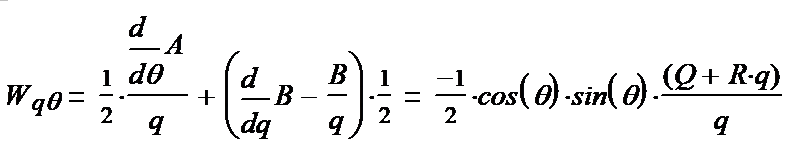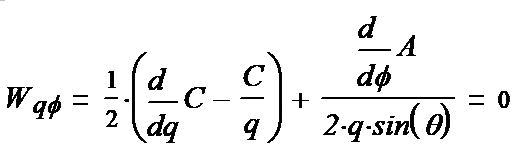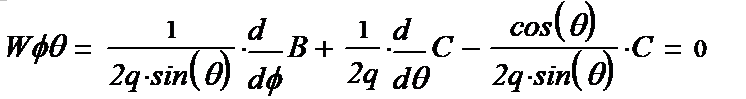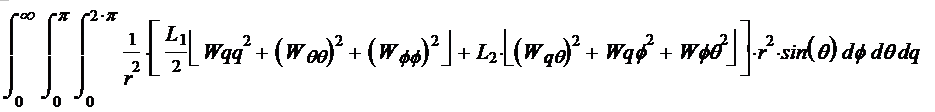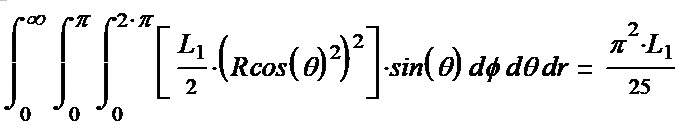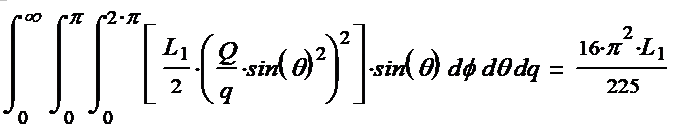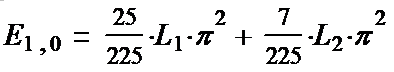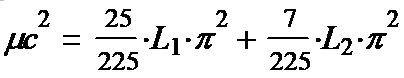|
Назад Главная страница Оглавление Далее
Calculation of the lok energy (1,0). Below
this procedure is shown for the simple case
j
= 1 and m
= 0. What kind of particle, we do not yet know.
(1-22*)
The
coefficient under the square root is temporarily omitted. Put it in
the end. What is the coefficient
k.
This is nothing more than a link between
ω
in the vibrational part of the solution and the radial coordinate in
the Bessel function:
ω = k * c,
c
is the speed of light. The physics is such that in each particle (in
each solution), due to physical reasons, the frequency of the wave
traveling in a circle is set. Physical causes are determined by the
form of the solution, and the way the solution is wound up on
itself, and how the whole system stabilizes to a stable state. Also,
particles have excited states. This issue has not yet been
investigated. This can only be observed. Thus, all further solutions
and formulas are only an illustration of the state in which all the
wave vortices are located = loks
= elementary particles.
(1-23*) (1-24*) (1-25*) We introduce useful notation:
We write out the components of the tensor (1-15):
(1-26*) (1-27*) (1-28*) (1-29*) (1-30*) (1-31*)
Now try to write out the formula for energy: The energy of lok j=1 и m=0 in spherical coordinates:
(1-32*)
Here:
in the center, in the square bracket is the expression for the
energy density itself. On the right after the parenthesis is the
expression for the volume element. Left before the bracket is the
expression (1 / r2) for the law of winding.
We
get a solution:
(1-34*) This
formula is something that relates the elastic properties of Gukuum
L1
and
L2
with
the mass of (supposed!) elementary particles and the angular
velocity of their rotation. Applying the formula of Lord Kelvin, we
obtain:
(1-35*)
While
we do not know what kind of particle it is. Two such equations for
two different loks will make it possible to determine
L1
and L2
of
cosmic Gukuum. Оглавление Далее Страница размещена на сайте в мае 2005 года |