|
Назад
Главная страница
Оглавление
Далее
Photon, radio
waves, neutrinos.
Published:
http://vixra.org/abs/1803.0690
https://www.academia.edu/36275759/Photon._Shape_internal_arrangement_and_physical_properties
https://www.academia.edu/36275775/Photon._Shape_internal_arrangement_and_physical_properties
Old rezults.
Abstract.
Several formulas are obtained describing objects moving at
the speed of light. These formulas are particular solutions
of the wave equation, in spherical and cylindrical
coordinates. Conclusions about the belonging of these
solutions to photons or neutrinos or radio waves have not
yet been made.
The initial equations.
So, let us recall the chapter on the varieties of
solutions of the wave equation. Again a single formula of
all matter, all Particles, all Fields and all Quantums of
our Universe:

(5-0)
Here,
W
is the displacement vector of the elastic cosmic gukuum
element.
c
is the speed of light or the velocity of transverse waves,
determined by the mechanical parameters of the gukuum.
Longitudinal waves are not considered.
We start from absolutely reliable ([10]) results:
solutions of the wave equation for displacement, and also
physical formulas for an elastic body.
The same equation (5-0), the Uniform formula of all
matter, of all Particles, of all Fields and all Quanta of
our Universe, but expressed in the Cartesian coordinates of
the projections
Wi
of the displacement vector
W:

(5-1) ≡ (5-0)
Wi is the
projection of the displacement vector of the elastic
space.
Different types of solutions of equation (5-1)
correspond to different types of oscillatory processes.
In particular,
a) waves propagating to infinity at the speed of light,
b) waves localized, standing, vortex. Etc.
And these kinds of solutions are not exhausted. It is
very likely that some types of localized solutions can
also propagate to infinity at a speed close to the speed
of light. And it is very likely that many waves
propagating to infinity have a localized structure. All
these kinds of oscillations really exist in the Elastic
Universe, creating a visible variety of material
objects.
More
later. There is an assumption that in general all material
objects existing in our perception are localized. Including
electromagnetic waves.
Definition. One of the solutions of equation (5-1) is a
localized wave. This is a vortex-shaped wave object
localized in space - a field of stresses in Gukuum.
The main solution of the wave equation, which is used in the
theory of gukuum to describe localized waves, is the
sinusoidal spherical standing waves.
We work in spherical coordinates:
x=r·sinθ·cosφ,
y=r·sinθ·sinφ,
z=r·cosφ
(5-2)
A
particular solution of the wave equation, spherical standing
waves:

(5-3)
k is the
wave number.
i=1,2,3 (Cartesian);
j,m=0,1,2, ...;
Cj,
are arbitrary;
ω=c•k;
c is the
speed of light.
True,
a preliminary check shows that formally the energy integral
over the given formula does not converge. But as we have
seen before, you can not simply formally integrate.
Necessarily somewhere there will be "winding", which must be
taken into account. This check will have to be done better
in the future.
The following reasoning may apply. At the time of
formation, the shape of the photons is far from the formula
described above. Then, during the flight, they gradually
relax to a normal form and all this occurs in motion at
light speed. That is, the photon is already in the process
of flying gradually grows this "divergent as an integral
tail." This tail, despite the fundamental infinity of its
energy in infinite time, remains at any finite time not too
large in percentage to the energy of the photon center.
It is also possible that one has to take into account the
cosmic background.
Objects in cylindrical coordinates. They too can be
moving.
Class 4 (optional). A similar situation with an even
lightning. We work in cylindrical coordinates:
x=ρ·cosφ,
y=ρ·sinφ,
z=z ;
(5-16)

(5-10)
k is the wave number.
i=1,2,3 (Cartesian);
j,m=0,1,2, ...;
Cj, are arbitrary;
ω=c•k;
c is the speed of light.
True,
a preliminary check shows that formally the energy integral
over the given formula does not converge. But as we have
seen before, you can not simply formally integrate.
Necessarily somewhere there will be "winding", which must be
taken into account. This check will have to be done better
in the future.
The following reasoning may apply. At the time of
formation, the shape of the photons is far from the formula
described above. Then, during the flight, they gradually
relax to a normal form and all this occurs in motion at
light speed. That is, the photon is already in the process
of flying gradually grows this "divergent as an integral
tail." This tail, despite the fundamental infinity of its
energy in infinite time, remains at any finite time not too
large in percentage to the energy of the photon center.
It is also possible that one has to take into account the
cosmic background.
Objects in cylindrical coordinates. They too can be
moving.
Class 4 (optional). A similar situation with an even
lightning. We work in cylindrical coordinates:
x=ρ·cosφ,
y=ρ·sinφ,
z=z ;
(5-16)

(5-17)
This solution mathematically should be a kind of endless
garland of sausages along the
Z
axis. And if it is physically feasible, then it is very
likely that this object will turn out to be an Anniversary
Lightning. Some analysis of this decision is made, here it
is not given. The energy integrals converge (in terms of one
sausage). But we postpone it for the future.
In addition to the cylindrical solution, one can
certainly perform work as well as over a spherical solution.
That is, similarly to find those three types of solutions,
and the corresponding objects that generate the solution of
the wave equation in cylindrical coordinates. In a
cylindrical solution, you can use variables
(z±ωt)
и
(ρ±ωt):

and

What is the
physical meaning of the formulas obtained, so far we
will not guess. Where is the photon, where the neutrino,
where the other objects moving at the speed of light.
This is the business of the future.
The processes in which photons are born.
Based on physical considerations and common
sense, we can assume the following.
1) There are various processes in which photons or
neutrinos are formed. And photons and neutrinos each
time different (at the initial moment) are formed
according to their properties and form. And not only
photons and neutrinos, but other particles, even unknown
ones, are possible. Examples of such processes are:
- Annihilation of a particle + antiparticle when all the
turns of localized wave formations (ie, particles)
straighten out at once. In the chapter on antimatter,
the meaning of this phrase will be clarified.
- The transition of an electron
in an atom from one level to another, when, figuratively
speaking, individual loops of localized wave formations
(ie, particles) straighten out. In this number, the
turns of some temporary, transitional states of
particles can "straighten out". This is the subject of
future research.
- Electric current oscillations in radiating antennas,
when photons are generated by an electromagnetic field.
- Interactions of high-energy particles with the
emission of neutrinos and other objects.
- Decay of short-lived particles.
2) Photons can have different shapes in their formation.
Thus, photons produced by intra-atomic processes or
during annihilation can be characterized by high
compactness and unidirectional motion. But photons from
the radio range can be spherically propagated, with a
rapid decrease in intensity. What we see every day in
telephone communication and radio communication. The
possibility of other forms will be established by the
current generation of young scientists.
3) Taking into account that the
photons arising in the annihilation processes are formed
when the localized rotating wave layers are
straightened, it is possible that the resulting
amplitude of the oscillations consists of the amplitudes
of the layers that alternate in the direction of
rotation. Here it is necessary to think, these
differently directed layers - they are composed among
themselves and then fly in one direction, or immediately
fly in different directions ?! Yes, actually,
antiparticles also need a serious mental analysis. And
suddenly, when particles collide with antiparticles, all
the "positively directed" (in the sense of rotation,
according to the rule of the drill) the layers from both
particles fly in one direction, and "negatively
directed" from both particles fly to the other side? Or
are they first added together, and then each amount
flies in different directions?
4) Taking into account that the photons formed in the
annihilation processes are formed during the
"straightening" of the localized rotating wave layers,
which decrease (in amplitude) with the number (distance
from the rotation axis), it can be assumed that
sometimes, and maybe always, Photons have the type of
wave peleton whose amplitude is distributed (at
considerable distances) approximately of the type as 1/r,
where
r is the distance from the
"core" of the photon. Like this. Here there is a wave
and corpuscular essence of a photon.
5) A photon, unlike elementary
particles, is not something unambiguous, repetitive and
stable. Each photon has a date of birth and the date of
death - when it is discovered. The spectrum of possible
photon energies (possibly) is continuous and depends on
the difference in the energies of the interacting
particles or energy levels.
Someone on the forum asked a question: here is a
photon flying away from us into the black infinity of
space. And now no one will ever see him. So he is or is
he already gone? And will not all the photons fly away
in this way? The answer is this. At this moment, from
the infinity somewhere from another place the same
photon arrives, so we have nothing to worry about. The
equilibrium in the infinite universe has been
established for the whole previous minus - its infinite
history. And there is a photon or it is not present in
any point of space we do not know yet it we will not
find out. But as soon as we find it, here it is not
there at once.
6) Neutrinos, in all likelihood, are also a variety of
the same class of objects. It is not yet known what is
their commonality (except the speed of propagation), and
what is their difference. This will also be established
by the current generation of young scientists.
Red
shift. Hypothesis.
At the time of formation, the
shape of the photons is far from the formulas described
above. Further photons in the process of flight, perhaps,
gradually relax to some normal form. That is, the photon is
already in the process of flying gradually grows some tail,
which is becoming longer and longer. This tail, despite the
fundamental infinity of its energy in infinite time, remains
at any finite time not too large (as a percentage of the
energy of the photon center). That is, photons remain with
the finite, initially given energy, during the whole flight.
In addition, if the energy for growing the tail is taken
from the photon itself (and not from the cosmic background),
then the energy of the central part of the photon slowly
decreases. It is possible that in this phenomenon, the
spreading of a photon in flight, and there is a cause of
cosmic "redshift".
Equilibrium in the universe.
Well, are there any reverse processes of collision of
photons and their transformation again into elementary
particles? - Probably yes. Definitely: yes. This is the
universal mobile equilibrium. These photons will sooner or
later successfully collide (again: perhaps with triple
collisions, involving neutrinos and other particles, albeit
rarely, no one in the universe and does not rush).
Thus, the equilibrium process between the number of
photons and the number of neutrons in the entire universe is
realized. (See the chapter on black holes). It is only
necessary to overaccumulate neutrons, as they begin to
thicken around some centers in order to shrink into a black
hole. But, alas, this is not to be. For they in the majority
will burn down and will turn to photons. Which will be
stupid to fly through the universe and again somewhere will
collide, forming a pair of neutrons.
New rezults.
Photon. Shape, internal arrangement and
physical properties.
Abstract.
An attempt has been made to explain theoretically the
properties of a photon from the position of the theory of
the Elastic Universe.
We see photons, know
photons, know the action of photons, know the properties of
photons, we know the dual, corpuscular-wave character of
photons. We do not know only one thing: what a photon looks
like under a strong microscope. Now we will try to do it.
First an example of acoustics. Imagine that we are
inside the sound wave and move with it. Modern technology
allows you to depict a sound wave on an equalizer:

Fig.1.
Imagine that we can see the differences in
the density of air in the sound. And so we fly along with
the sound wave, with the speed of sound and see this sound
wave, all its oscillations, approximately as in the figure
above. Let from this place each reader imagines to itself a
picture how he understands all process. To the best of my
scientific training.
What do we see in the process of flying with sound? - We
see a stationary picture of sound. We fly with the sound
over forests, fields, houses, cities, bridges. Landscapes
change around. But the picture of the sound wave that
surrounds us does not change. Well, except that the sound
fades with time, that is, the colors of the sound landscape
become faded and gradually fade. But the picture of the
sound around us is stable and unchanging. We do not see
around us any fluctuations in the density of air. We see air
seals, permits, see their wavy character. All as in the
picture above. But we do not see around ourselves no
hesitation. The whole sound is distributed as a whole.
From a domestic point of view, if we shouted, for example,
the word "Locomotive" (Fig.1), then it appeared on the
equalizer as some oscillatory region. And then, whenever and
wherever we listen to this sound, in 1 second or 30 seconds,
it will be the same word "Locomotive". Although over time,
the volume will decrease.
The theory of wave propagation in the three-dimensional
elastic medium, which textbooks offer us, reports that if
the initial state was a localized perturbation, then it
spreads like a spherical wave. And with a sharply marked
beginning and end, without "aftereffect" (that is, without
damping, in contrast to plane waves).

Classical
presentation of the propagation of the initial perturbation
Т0,
from point
S,
illustrated in Figures 3 and 4
(taken
from the textbook).
Do not go into too many of these terms. I.e:
1) First, the initial perturbation
Т0
(Fig.3)
does not reach the point
M0
,
and there is no disturbance at this point.
2) Then the initial perturbation reaches the point
M0
,
and at this point a disturbance appears.
3) After some time to the point
M0
the back boundary of the initial perturbation already
reaches and at this point the point
M0
the
disturbance completely ceases. This part of the presentation
is quite convincing.
Further, it is concluded that the initial perturbation
located in the region
Т0
,
will necessarily spread in a spherical manner
(Fig.4),
decreasing in intensity, and as if in the course of time, in
the future crosses every point of space.
The theory about the one-dimensional wave equation tells
us about the same thing. Instead of the three-dimensional
model of perturbation propagation depicted in Fig. 4, we
have a one-dimensional model. This model is described by a
one-dimensional wave equation.
(1-1)
Where
W
=
W(x,t)
- displacement at the point of the medium,
c is the speed of light.
As is known, the solution of a one-dimensional wave
equation retains its original shape during motion. The
solution of the one-dimensional wave equation has the form:
|
W(x,t)
=
f1(x-ct)
+
f2(x+ct) |
(1-2)
Where
f1
and
f2
are determined by the initial conditions,
and
f1
refers to one object of two flying away, and
f2
refers to the second object.

Fig.5.
As the solution of
the one-dimensional wave equation suggests, objects are born
in pairs. This is also observed in three-dimensional
physics. Often photons are born in pairs. In this the roots
of such a legend as the entanglement of photons. There is no
confusion. But there are pairs of photons flying in
different directions.
What is the conclusion from all the arguments that have
been made? The conclusion is this: if we are in the
reference frame of a moving wave object, whether it is
one-dimensional or three-dimensional, we see around us a
stationary picture of the deformations (or stresses) of the
environment. No hesitation in time! Here falling drops of
water from a tap with water can fluctuate during the flight.
And if we sit in such a drop, and if the drop is flying for
a long time, then we will see how our drop changes its shape
during the flight. The drop vibrates its shape. But if we
are sitting inside a sound wave, or inside a one-dimensional
wave, or inside an electromagnetic disturbance propagating
in a gukuum (= in space), then we will not see any
oscillations around ourselves.
Now we are
theoretically prepared to understand what a photon is. A
photon is a disturbance in the gukuum, which propagates at a
rate determined by the properties of the gukuum. That is,
with the speed of light. In the process of moving, the
photon keeps its shape exactly. But what is this form? Here
again the analogy from the world of sound (Fig.1). If we
shouted the word "Locomotive" in an electromagnetic way,
then this word will be distributed in space. That is, the
oscillogram Fig.1 will be saved. Similarly, photons!
PHOTON FORM DETERMINED
BY THE PROCESS OF ITS BIRTH.
Photons are like
sound words in the gukuum, flying in space. They can be
depicted on a spatial equalizer. They fly from a distant or
near past and carry information about the process of their
creation.
How is the photon created? There are a lot of processes.
1. The most common. The transition of an electron inside the
molecule to a lower level with the emission of an energy
quantum (= photon).
2. Collision of particles with a change in energy. The laws
of conservation of momentum and energy require one more
particle, and this particle turns out to be a photon.
3. Nuclear reactions.
4. Process of particle annihilation. Gif:
http://i.yapx.ru/BDq5J.gif
http://universe100.narod.ru/u270/b15.gif
http://universe100.narod.ru/u210/image017.gif
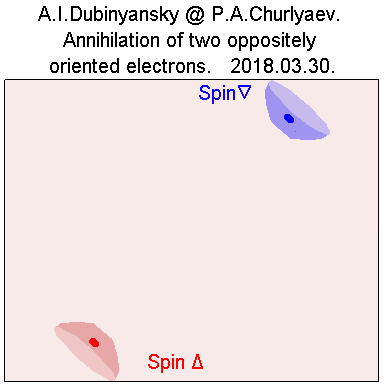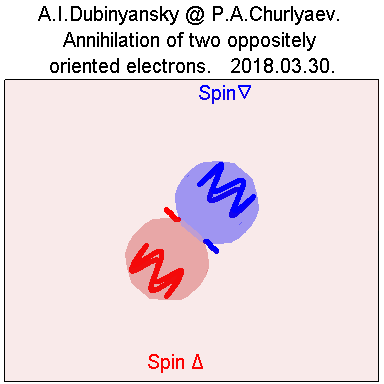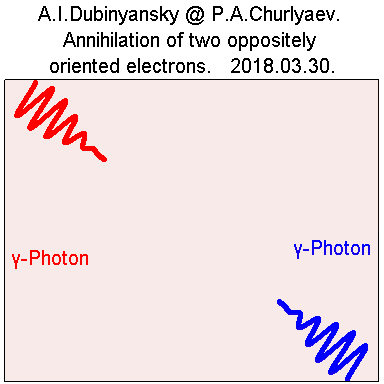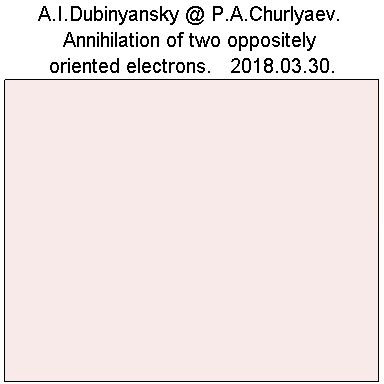
Fig.6.
As can be seen from
the listed processes, they are all fast, they all have a
beginning and an end, they all have a clear limitation in
time and energy. For this reason, all photons have a clear
energy and shape.
We have not yet gone into a rigorous exposition of the
essence of antimatter in the theory of the elastic universe.
The working model is as follows: two elementary particles
collide "forehead", one of which, according to the rule of
the drill, is twisted in one direction, and the second one
in the other. What is this collision process? This process
consists in the fact that the vortex, swirling localized
waves of each of these two wave vortices, rotating towards
each other, suddenly interact, "straighten out" and all
their motion from the circular turns into a linear one.
Almost instantly. Two photons are formed, which are
scattered strictly one line in different directions. And
practically each of these photons has a polarization in one
direction, presumably along the axis of rotation of the
former particle.
In accordance with the annihilation process, the shape of
the photons produced in this process is approximately the
same if we consider only the electric or only the magnetic
component of the photon wave:
Gif-image:
http://i.yapx.ru/BJWTe.gif
http://universe100.narod.ru/u210/Photon-01.gif
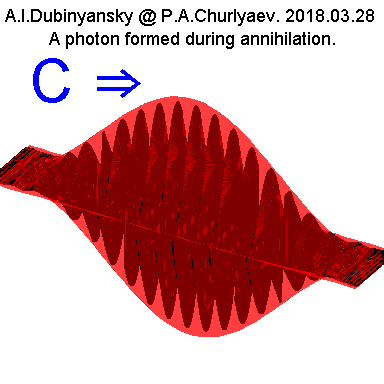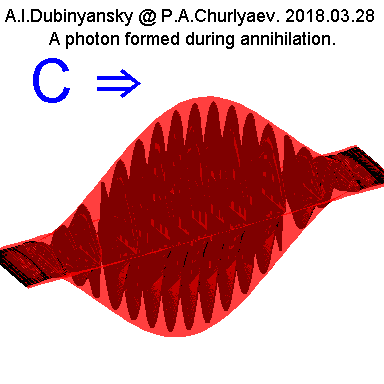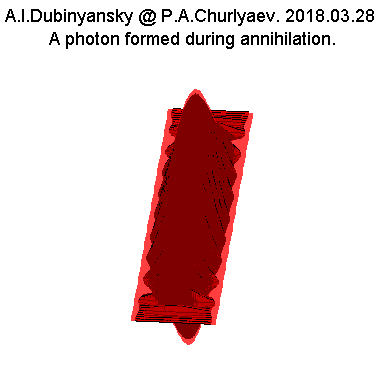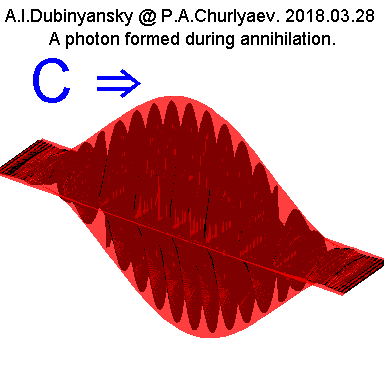
Fig.7.
That is, there is a
growth region and an attenuation region of the amplitude of
the electric or magnetic component. In its thickness, such
photons, formed as a result of annihilation of electrons,
are apparently just of the order of the electron diameters.
All other parameters are also quite specific.
With the image of both the magnetic and electrical
components, the photon looks like this:

Fig.8.
You can not consider
photons as flat as in Fig.6 or as consisting of two planes
as in Fig.8. A photon is a figure that is smooth and
voluminous throughout the space. However, there are
directions in which the maximum values of the electric or
magnetic component are realized, and the directions
perpendicular to them, where these quantities are minimal.
Depending on the process of its creation, or the
external influence on the photon during its flight through
some medium, it is possible to obtain such photons:

Fig.9.
But this again does
not mean that such a photon is flying and spiraling. No. He
flies without changing form and orientation. But at the
moment of its registration, at the moment of its passage
through some medium, through the detector, it shows similar
twisted properties.
FORM PHOTON DOES NOT
CHANGE IN THE MOVEMENT PROCESS.
About the speed of a
photon. All fragments of the photon fly in one direction, do
not have any transverse vibrations and movements. For this
reason, the speed of the whole object = photon is the same
and equal to the speed of light.
About the mass of the photon. From a comparison of the
photon described here with wave vortices, it can be seen
that photons do not have points of singularity in density.
That is, they do not have mass formation centers. Therefore,
they have no rest mass. They do not have a strict and
uniform spatial form. Each photon is individual, has its own
form, energy, has its date and place of birth, has the
parent process in which it was born. It is possible to
introduce a classification of the processes of photon
formation and call this classification the "nationality" of
the photon. This will facilitate memorization.
You should remember
about the "Dubinyansky field". The electric and magnetic
fields of a photon do not exhaust all fields in space,
including a photon. After all, the displacement of the
gukuum has three dimensions. Therefore, it is quite possible
that a photon has a third component of the field, in the
direction of its motion. Apparently this field is
longitudinal, rapidly decaying with distance. Since
longitudinal waves have a higher speed than transverse
waves, and since it decays with distance, the Dubinyansky
field in the photon quietly flies along with the photon.
However, this field can detect itself in some experiments.
For example, in the experiments of Aaronov-Bohm.
Concerning the
formulas we previously proposed for a photon or neutrino,
they turned out to be of little relevance to reality. There
are no single-valued photon formulas. However, there is some
classification of the processes in which photons are formed.
And this classification creates a certain number of types of
photon forms.
In occasion of wave or corpuscular properties of a
photon. It depends on the process in which the photon
participates. If this is a process of energy exchange, then
the photon manifests itself as a particle. But if a photon
passes through narrow slots whose width is comparable with
the photon size, then the photon form begins to appear,
which has the form of a wave (Fig.5). Accordingly, the
properties of the photon become wave.
About the
neutrino. In fact, this is one of
the varieties of photons, specific forms and energies,
allowing to penetrate through material objects. Emerging in
specific processes. Since neutrinos occur in specific
processes, they may have a rather specific form. For each
process, the neutrino shape must be set separately.
Назад
Главная страница
Оглавление
Далее
Страница размещена на сайте в мае 2005
года |













